Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol (DHCP)
Dynamic Host Configuration Protocol(DHCP) is an application layer protocol which is used to provide:
- Subnet Mask (Option 1 – e.g., 255.255.255.0)
- Router Address (Option 3 – e.g., 192.168.1.1)
- DNS Address (Option 6 – e.g., 8.8.8.8)
- Vendor Class Identifier (Option 43 – e.g., ‘unifi’ = 192.168.1.9 ##where unifi = controller)
DHCP is based on a client-server model and based on discovery, offer, request, and ACK.
These messages are given as below:
- DHCP discover message –
This is a first message generated in the communication process between server and client. This message is generated by Client host in order to discover if there is any DHCP server/servers are present in a network or not. This message is broadcasted to all devices present in a network to find the DHCP server.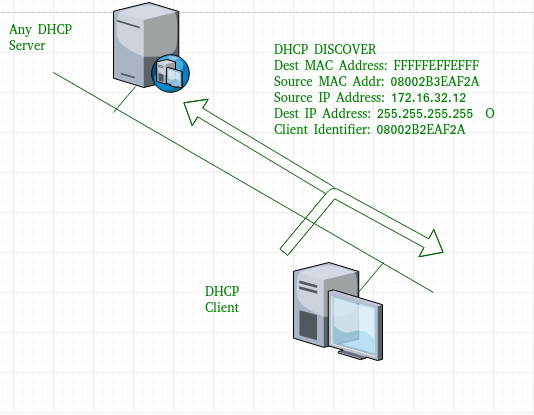
- DHCP offer message –
The server will respond to host in this message specifying the unleased IP address and other TCP configuration information. This message is broadcasted by server. Size of message is 342 bytes. If there are more than one DHCP servers present in the network then client host will accept the first DHCP OFFER message it receives. Also a server ID is specified in the packet in order to identify the server.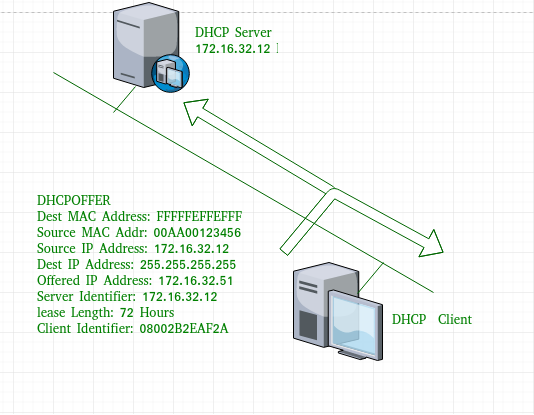
- DHCP request message –
When a client receives a offer message, it responds by broadcasting a DHCP request message. Note – This message is broadcast after the ARP request broadcast by the PC to find out whether any other host is not using that offered IP. If there is no reply, then the client host broadcast the DHCP request message for the server showing the acceptance of IP address and Other TCP/IP Configuration.
Note – This message is broadcast after the ARP request broadcast by the PC to find out whether any other host is not using that offered IP. If there is no reply, then the client host broadcast the DHCP request message for the server showing the acceptance of IP address and Other TCP/IP Configuration. - DHCP acknowledgement message –
In response to the request message received, the server will make an entry with specified client ID and bind the IP address offered with lease time. Now, the client will have the IP address provided by server.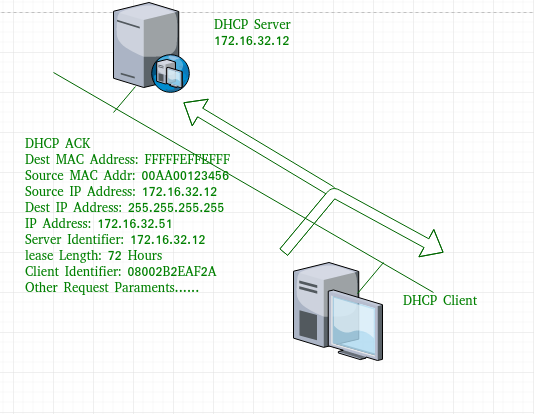
- DHCP negative acknowledgement message –
Whenever a DHCP server receives a request for IP address that is invalid according to the scopes that is configured with, it send DHCP Nak message to client. Eg-when the server has no IP address unused or the pool is empty, then this message is sent by the server to client. - DHCP decline –
If DHCP client determines the offered configuration parameters are different or invalid, it sends DHCP decline message to the server .When there is a reply to the gratuitous ARP by any host to the client, the client sends DHCP decline message to the server showing the offered IP address is already in use. - DHCP release –
A DHCP client sends DHCP release packet to server to release IP address and cancel any remaining lease time. - DHCP inform –
If a client address has obtained IP address manually then the client uses a DHCP inform to obtain other local configuration parameters, such as domain name. In reply to the dhcp inform message, DHCP server generates DHCP ack message with local configuration suitable for the client without allocating a new IP address. This DHCP ack message is unicast to the client.
Advantages – The advantages of using DHCP include:
- centralized management of IP addresses
- ease of adding new clients to a network
- reuse of IP addresses reducing the total number of IP addresses that are required
- simple reconfiguration of the IP address space on the DHCP server without needing to reconfigure each client
Disadvantages – Disadvantage of using DHCP is:
- IP conflict can occur
Reference:
No comments:
Post a Comment