- SMTP stands for Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
- SMTP is a set of communication guidelines that allow software to transmit an electronic mail over the internet is called Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
- It is a program used for sending messages to other computer users based on e-mail addresses.
- It provides a mail exchange between users on the same or different computers, and it also supports:
- It can send a single message to one or more recipients.
- Sending message can include text, voice, video or graphics.
- It can also send the messages on networks outside the internet.
- The main purpose of SMTP is used to set up communication rules between servers. The servers have a way of identifying themselves and announcing what kind of communication they are trying to perform. They also have a way of handling the errors such as incorrect email address. For example, if the recipient address is wrong, then receiving server reply with an error message of some kind.
Components of SMTP
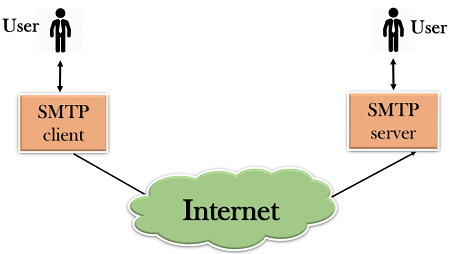
- First, we will break the SMTP client and SMTP server into two components such as user agent (UA) and mail transfer agent (MTA). The user agent (UA) prepares the message, creates the envelope and then puts the message in the envelope. The mail transfer agent (MTA) transfers this mail across the internet.
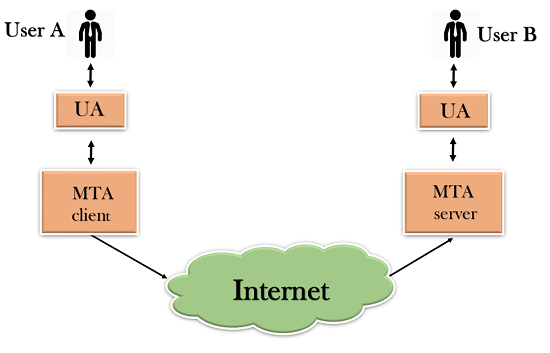
- SMTP allows a more complex system by adding a relaying system. Instead of just having one MTA at sending side and one at receiving side, more MTAs can be added, acting either as a client or server to relay the email.
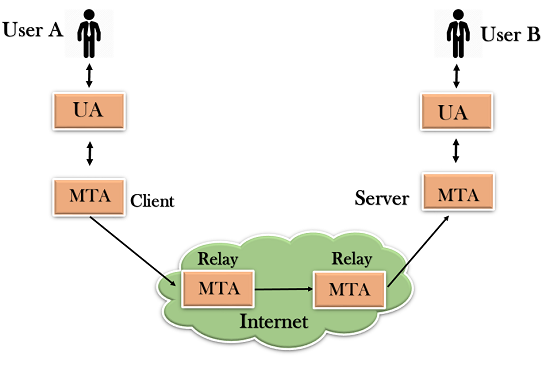
- The relaying system without TCP/IP protocol can also be used to send the emails to users, and this is achieved by the use of the mail gateway. The mail gateway is a relay MTA that can be used to receive an email.
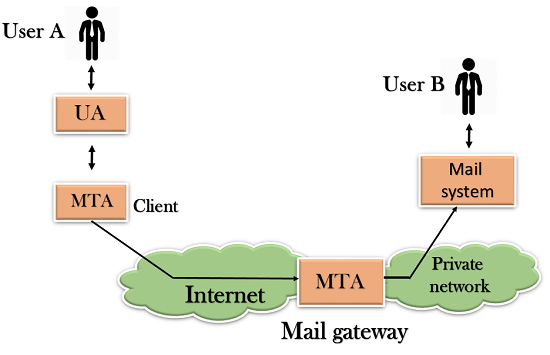
Working of SMTP
- Composition of Mail: A user sends an e-mail by composing an electronic mail message using a Mail User Agent (MUA). Mail User Agent is a program which is used to send and receive mail. The message contains two parts: body and header. The body is the main part of the message while the header includes information such as the sender and recipient address. The header also includes descriptive information such as the subject of the message. In this case, the message body is like a letter and header is like an envelope that contains the recipient's address.
- Submission of Mail: After composing an email, the mail client then submits the completed e-mail to the SMTP server by using SMTP on TCP port 25.
- Delivery of Mail: E-mail addresses contain two parts: username of the recipient and domain name. For example, vivek@gmail.com, where "vivek" is the username of the recipient and "gmail.com" is the domain name.
If the domain name of the recipient's email address is different from the sender's domain name, then MSA will send the mail to the Mail Transfer Agent (MTA). To relay the email, the MTA will find the target domain. It checks the MX record from Domain Name System to obtain the target domain. The MX record contains the domain name and IP address of the recipient's domain. Once the record is located, MTA connects to the exchange server to relay the message. - Receipt and Processing of Mail: Once the incoming message is received, the exchange server delivers it to the incoming server (Mail Delivery Agent) which stores the e-mail where it waits for the user to retrieve it.
- Access and Retrieval of Mail: The stored email in MDA can be retrieved by using MUA (Mail User Agent). MUA can be accessed by using login and password.
OR
he SMTP model is of two type :
- End-to- end method
- Store-and- forward method
The end to end model is used to communicate between different organizations whereas the store and forward method are used within an organization. A SMTP client who wants to send the mail will contact the destination’s host SMTP directly in order to send the mail to the destination. The SMTP server will keep the mail to itself until it is successfully copied to the receiver’s SMTP.
The client SMTP is the one which initiates the session let us call it as the client- SMTP and the server SMTP is the one which responds to the session request and let us call it as receiver-SMTP. The client- SMTP will start the session and the receiver-SMTP will respond to the request.
Model of SMTP system
The client SMTP is the one which initiates the session let us call it as the client- SMTP and the server SMTP is the one which responds to the session request and let us call it as receiver-SMTP. The client- SMTP will start the session and the receiver-SMTP will respond to the request.
Model of SMTP system
In the SMTP model user deals with the user agent (UA) for example Microsoft Outlook, Netscape, Mozilla, etc. In order to exchange the mail using TCP, MTA is used. The users sending the mail do not have to deal with the MTA it is the responsibility of the system admin to set up the local MTA. The MTA maintains a small queue of mails so that it can schedule repeat delivery of mail in case the receiver is not available. The MTA delivers the mail to the mailboxes and the information can later be downloaded by the user agents.
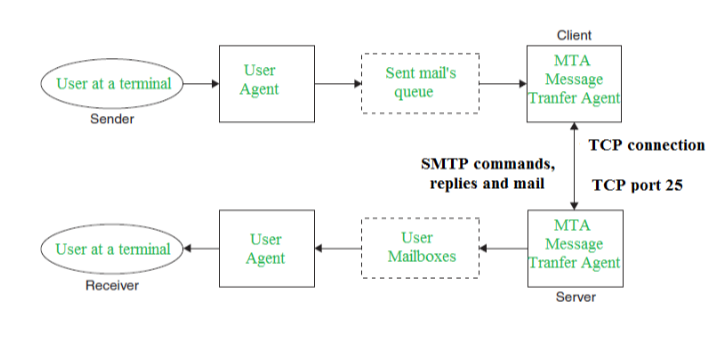

Both the SMTP-client and MSTP-server should have 2 components:
- User agent (UA)
- Local MTA
Communication between sender and the receiver :
The senders, user agent prepare the message and send it to the MTA. The MTA functioning is to transfer the mail across the network to the receivers MTA. To send mail, a system must have the client MTA, and to receive mail, a system must have a server MTA.
SENDING EMAIL:
Mail is sent by a series of request and response messages between the client and a server. The message which is sent across consists of a header and the body. A null line is used to terminate the mail header. Everything which is after the null line is considered as the body of the message which is a sequence of ASCII characters. The message body contains the actual information read by the receipt.
The senders, user agent prepare the message and send it to the MTA. The MTA functioning is to transfer the mail across the network to the receivers MTA. To send mail, a system must have the client MTA, and to receive mail, a system must have a server MTA.
SENDING EMAIL:
Mail is sent by a series of request and response messages between the client and a server. The message which is sent across consists of a header and the body. A null line is used to terminate the mail header. Everything which is after the null line is considered as the body of the message which is a sequence of ASCII characters. The message body contains the actual information read by the receipt.
RECEIVING EMAIL:
The user agent at the server side checks the mailboxes at a particular time of intervals. If any information is received it informs the user about the mail. When the user tries to read the mail it displays a list of mails with a short description of each mail in the mailbox. By selecting any of the mail user can view its contents on the terminal.
The user agent at the server side checks the mailboxes at a particular time of intervals. If any information is received it informs the user about the mail. When the user tries to read the mail it displays a list of mails with a short description of each mail in the mailbox. By selecting any of the mail user can view its contents on the terminal.
Reference:
No comments:
Post a Comment