An application layer protocol defines how application processes (clients and servers), running on different end systems, pass messages to each other. In particular, an application layer protocol defines:
- The types of messages, e.g., request messages and response messages.
- The syntax of the various message types, i.e., the fields in the message and how the fields are delineated.
- The semantics of the fields, i.e., the meaning of the information that the field is supposed to contain;
- Rules for determining when and how a process sends messages and responds to messages.
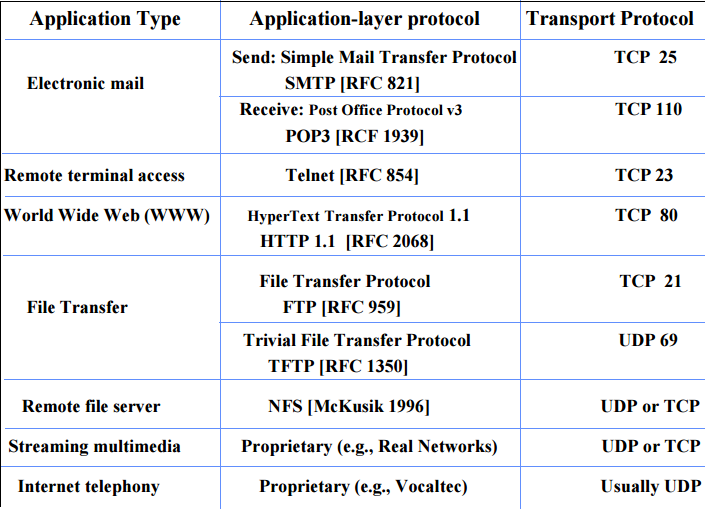
- One of the most popular network service is electronic mail (e-mail).
- The TCP/IP protocol that supports electronic mail on the Internet is called Simple Mail Transfer Protocol (SMTP).
- SMTP transfers messages from senders' mail servers to the recipients' mail servers using TCP connections.
- Users based on e-mail addresses.
- SMTP provides services for mail exchange between users on the same or different computers.
- Following the client/server model:
- SMTP has two sides: a client side which executes on a sender's mail server, and server side which executes on recipient's mail server.
- Both the client and server sides of SMTP run on every mail server.
- When a mail server sends mail (to other mail servers), it acts as an SMTP client.
- When a mail server receives mail (from other mail servers) it acts as an SMTP server.
- TELNET is client-server application that allows a user to log onto remote machine and lets the user to access any application program on a remote computer.
- TELNET uses the NVT (Network Virtual Terminal) system to encode characters on the local system.
- On the server (remote) machine, NVT decodes the characters to a form acceptable to the remote machine.
- TELNET is a protocol that provides a general, bi-directional, eight-bit byte oriented communications facility.
- Many application protocols are built upon the TELNET protocol
- Telnet services are used on PORT 23.
- FTP is the standard mechanism provided by TCP/IP for copying a file from one host to another.
- FTP differs form other client-server applications because it establishes 2 connections between hosts.
- Two connections are: Data Connection and Control Connection.
- Data Connection uses PORT 20 for the purpose and control connection uses PORT 21 for the purpose.
- FTP is built on a client-server architecture and uses separate control and data connections between the client and the server.
- One connection is used for data transfer, the other for control information (commands and responses).
- It transfer data reliably and efficiently.
- It is an extension of SMTP that allows the transfer of multimedia messages.
- If binary data is included in a message MIME headers are used to inform the receiving mail agent:
- Content-Transfer-Encoding: Header alerts the receiving user agent that the message body has been ASCII encoded and the type of encoding used.
- Content-Type: Header informs the receiving mail agent about the type of data included in the message.
- POP is also called as POP3 protocol.
- This is a protocol used by a mail server in conjunction with SMTP to receive and holds mail for hosts.
- POP3 mail server receives e-mails and filters them into the appropriate user folders. When a user connects to the mail server to retrieve his mail, the messages are downloaded from mail server to the user's hard disk.
- This is a protocol used mainly to access data on the World Wide Web (www).
- The Hypertext Transfer Protocol (HTTP) the Web's main application-layer protocol although current browsers can access other types of servers
- A respository of information spread all over the world and linked together.
- The HTIP protocol transfer data in the form of plain text, hyper text, audio, video and so on.
- HTTP utilizes TCP connections to send client requests and server replies.
- it is a synchronous protocol which works by making both persistent and non persistent connections.
- To identify an entity, TCP/IP protocol uses the IP address which uniquely identifies the connection of a host to the Internet.
- DNS is a hierarchical system, based on a distributed database, that uses a hierarchy of Name Servers to resolve Internet host names into the corresponding IP addresses required for packet routing by issuing a DNS query to a name server.
- However, people refer to use names instead of address. Therefore, we need a system that can map a name to an address and conversely an address to name.
- In TCP/IP, this is the domain name system.
- DNS in the Internet: DNS is protocol that can be used in different platforms.
- Domain name space is divided into three categories.
- Generic Domain: The generic domain defines registered hosts according, to their generic behaviour. Each node in the tree defines a domain which is an index to the domain name space database.
- Country Domain: The country domain section follows the same format as the generic domain but uses 2 characters country abbreviations (e.g., US for United States) in place of 3 characters.
- Inverse Domain: The inverse domain is used to map an address to a name.


No comments:
Post a Comment